Takeover Code
A takeover occurs when one company makes a successful bid to assume control of or acquire another.
The SC established under the Securities Commission Act 1993 is a self-funding statutory body charged with the function to supervise and regulate the development of the securities and derivatives markets in Malaysia.
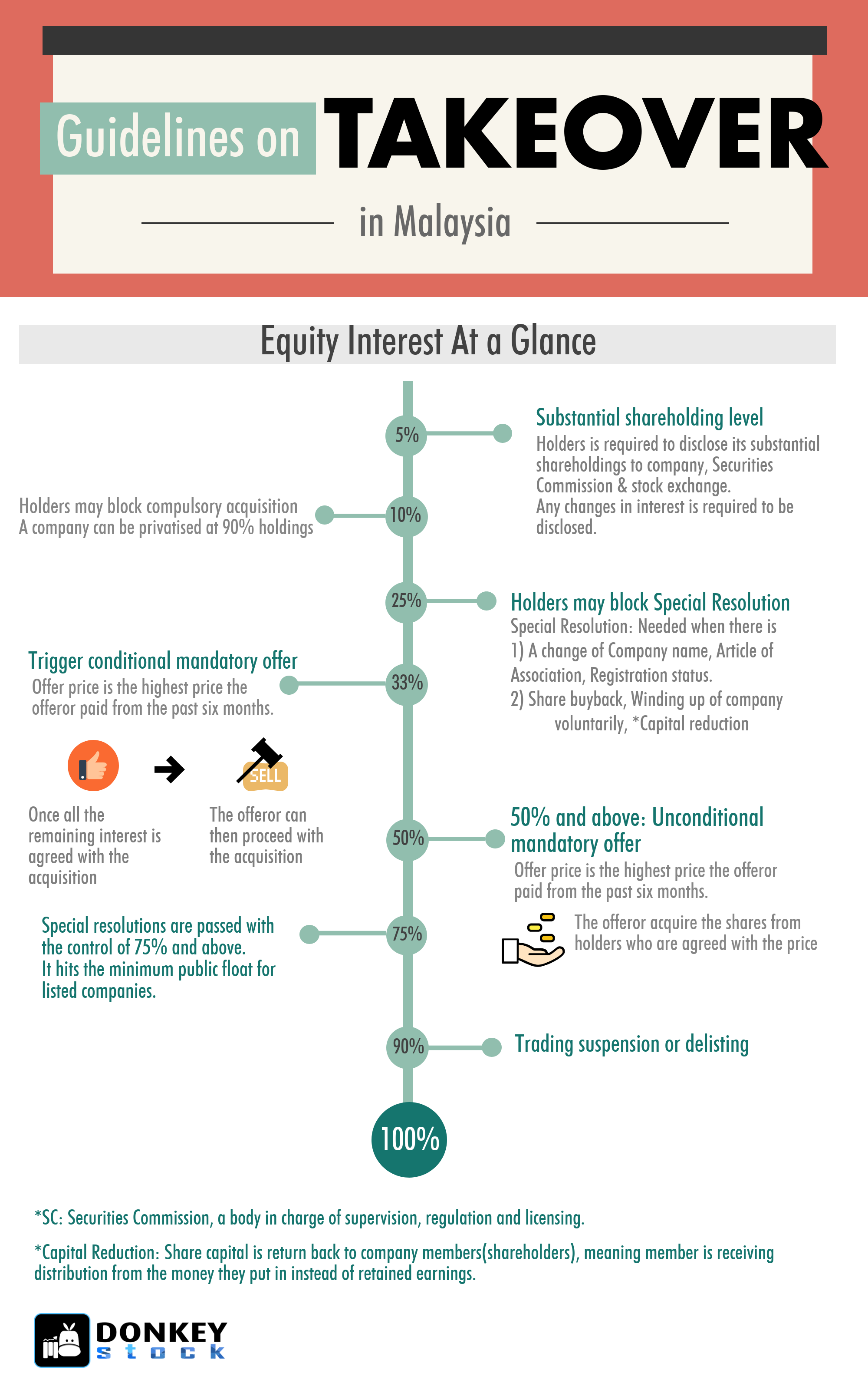
Here are some of the important percentage thresholds:
5% - Substantial shareholding level which requires the holder to disclose its substantial shareholdings to the company, SC, and stock exchange. Any changes in the interest of the substantial shareholdings are required to be disclosed.
10% - The holder may block the compulsory acquisition
25% - The holder may block special resolutions
A special resolution is required when there is a change of company name, Article of Association, registration status. It is also required when share buyback, winding up of company voluntarily, and *capital reduction.
*Capital reduction: Share capital is given back to company members(shareholders), Ie, a member is receiving a distribution from the money they put in instead of retained earnings
33% - trigger the obligation to extend a mandatory offer to acquire all the shares of the target company. The offeror proceeds with acquisition once all the remaining interest is agreed with the acquisition.
The offer price must be the highest price paid or agreed to pay in the last six months
>50% - Unconditional mandatory offer. The offeror acquires the shares from holders who are agreed with the price. Any shareholder who sells his share shall receive the money after 10 days.
The offer price must be the highest price paid or agreed to pay in the last six months
75% - Special resolutions are passed.
>75% - Minimum public float required for listed companies.
90% - Compulsorily acquire remaining shares of the target company. Trading of the shares may be suspended. The stock may also be de-listed by the stock exchange.
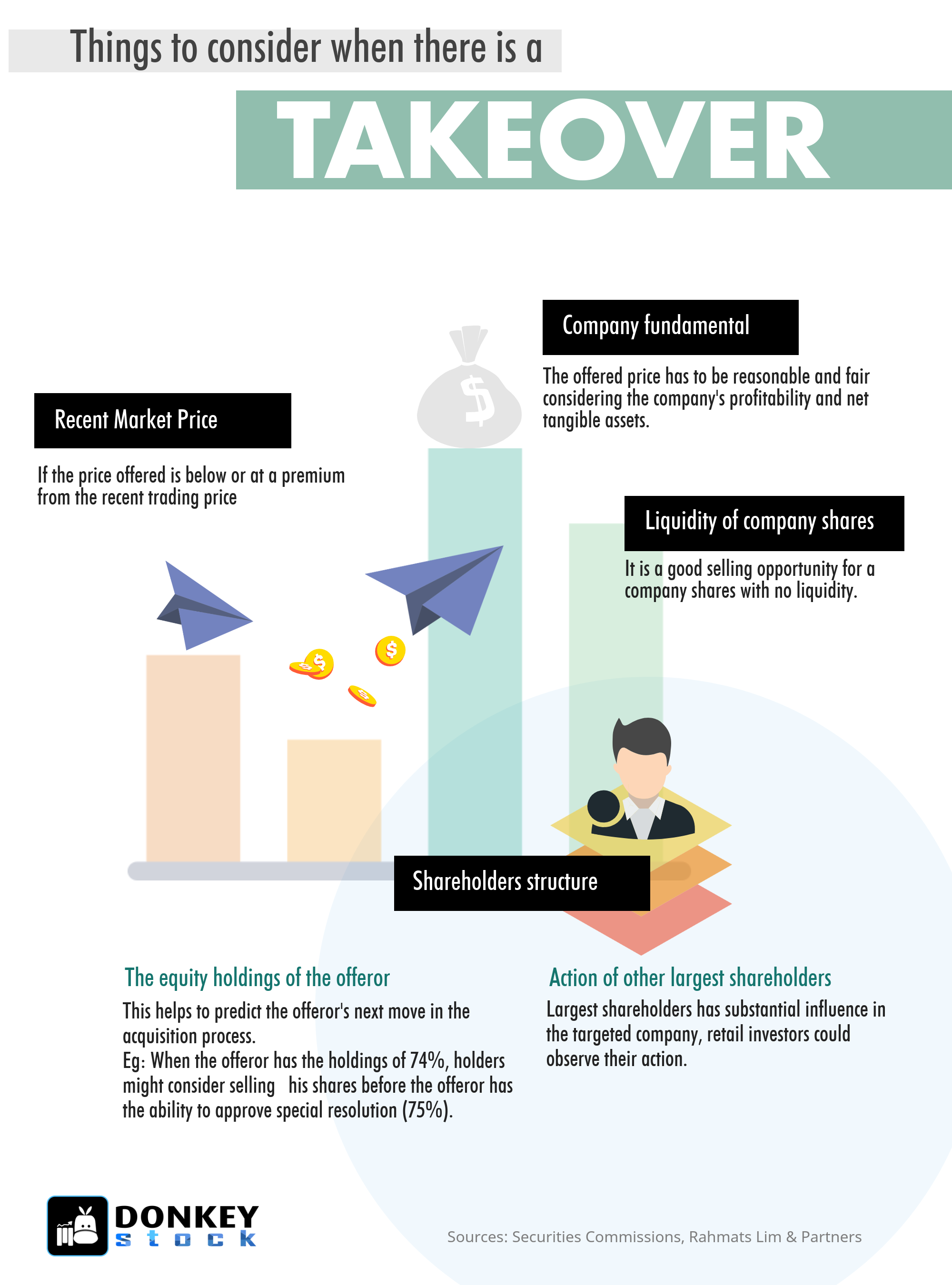
Things to consider when there is a Takeover
Recent Market Price: Consider if the price offered is below the trading price or above with a premium.
Company Fundamental: The offered price has to be reasonable and fair considering the company’s profitability and net tangible assets.
Liquidity of company shares: It is a good selling opportunity for a company shares with no liquidity.
The action of the other largest shareholders: If there are other largest shareholders, which have substantial influence in the targeted company, a retail investor could observe their action.
The equity holdings of the offeror: This helps to predict the offeror’s next move in the acquisition process. Eg: When the offeror has holdings of 74%, holders might consider selling their shares before the offeror has the ability to approve a special resolution (75%).
Related Guides
Mental for Value Investing
2022-01-18
|
Guide
|
Tags: Portfolio
Value investing is an investment strategy that involves picking stocks that appear to be trading for less than their intrinsic or book value.
Types of yield curve and its impact to the market
2021-11-26
|
Guide
|
Tags: Portfolio
Yield Curve is a graph that shows how bond yields and maturities are related. Here are the types of the yield curve, factors affecting the yield curve and how the market interpret the different type of yield curve
Types of Coal
2021-11-25
|
Guide
|
Tags: Portfolio
Coal is an abundant natural resource that can be used as a source of energy and is primarily used as fuel to generate electric power. The article illustrates the major types or ranks of coal


